CME
Decera Clinical Education Independent Conference Highlights of the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium 2025: Advanced and Metastatic Breast Cancer
Physicians: Maximum of 0.50 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit™
Released: February 20, 2026
Expiration: August 19, 2026
Activity
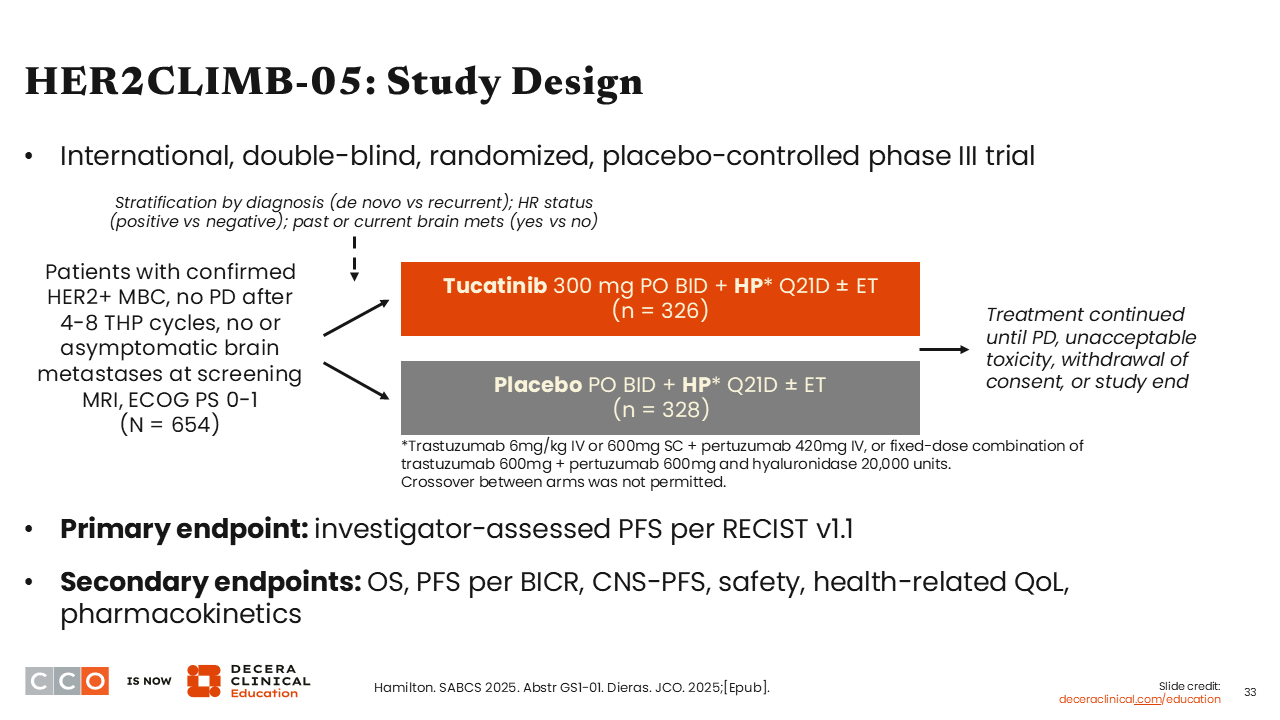
HER2CLIMB-05: Study Design
Sara M. Tolaney, MD, MPH:
I was excited to see new data presented at SABCS 2025 in the HER2-positive metastatic disease setting. The first highly anticipated study I would like to highlight is the phase III HER2CLIMB-05 trial.
HER2CLIMB-05 compared tucatinib plus trastuzumab and pertuzumab vs trastuzumab plus pertuzumab in the first-line maintenance setting in patients with HER2-positive MBC. Patients who took part in this trial had to have no evidence of disease progression after 4-8 cycles of THP. The primary endpoint of this study was investigator-assessed PFS per RECIST v1.1.25
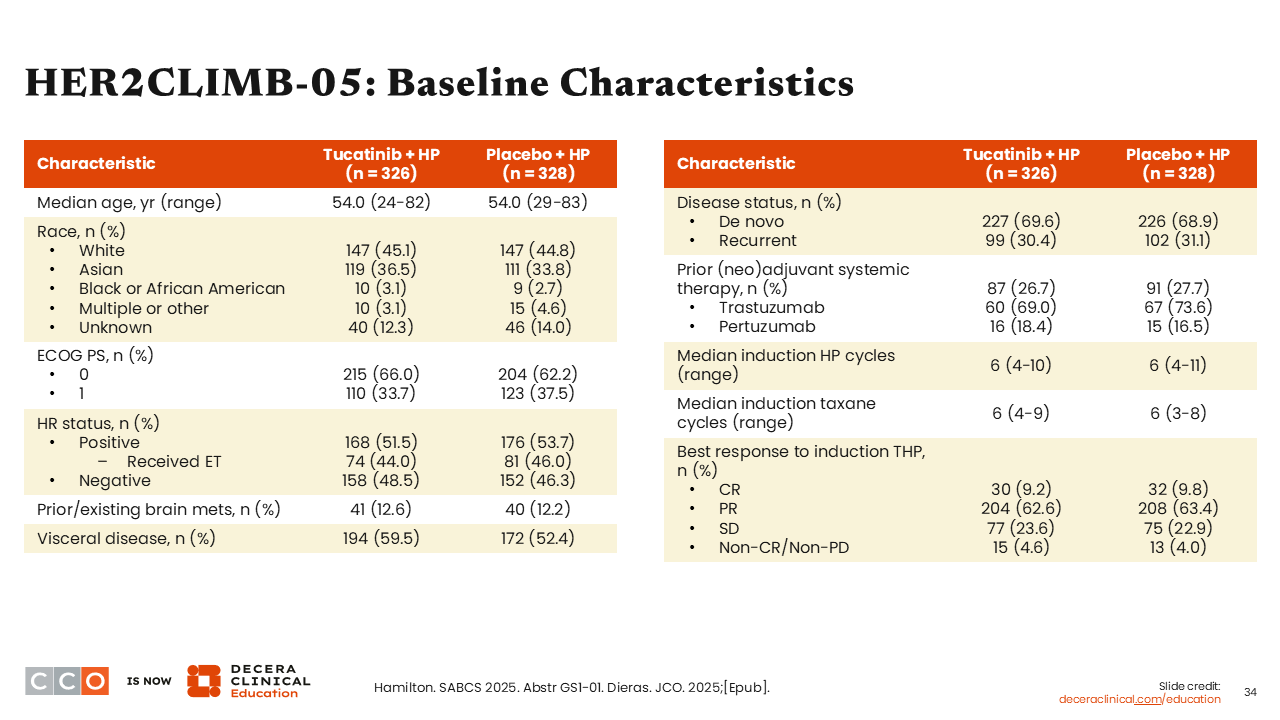
HER2CLIMB-05: Baseline Characteristics
Sara M. Tolaney, MD, MPH:
Approximately 50% of patients in the HER2CLIMB-05 trial had HR-positive disease and 12% had a history of brain metastases. Those with asymptomatic brain metastases could be either treated or untreated at time of enrollment. The proportion of patients with brain metastases at baseline (~12%) was modestly higher than in the DESTINY-Breast09 (5%-6%) or PATINA (4%) studies.26-28 That likely reflects a desire for enrolling patients with HER2-positive disease into a study on a CNS-penetrating tyrosine kinase inhibitor like tucatinib.
Looking at other baseline characteristics, the prevalence of de novo disease was approximately 70% for both treatment arms. This was higher than what we have seen in other first-line maintenance trials, which reported approximately 50% of patients with de novo disease.26-28
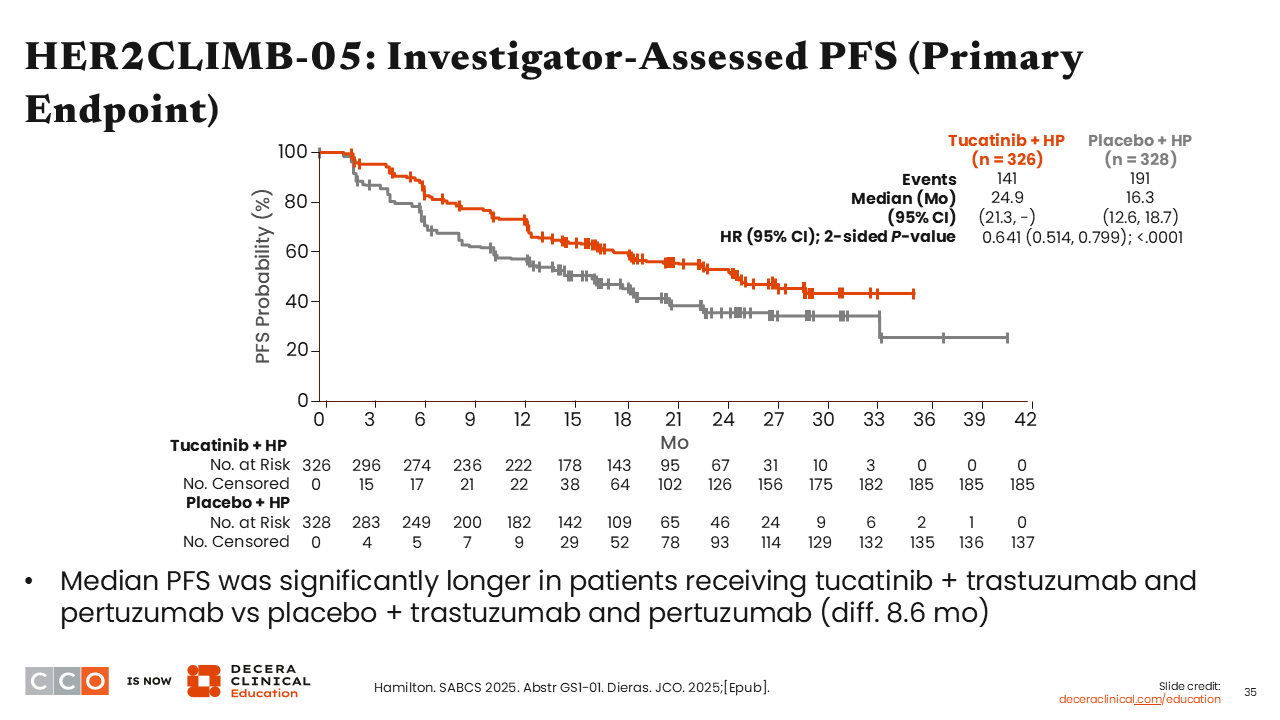
HER2CLIMB-05: Investigator-Assessed PFS (Primary Endpoint)
Sara M. Tolaney, MD, MPH:
I was impressed by the reported 8.6-month absolute improvement in PFS (median PFS: 24.9 vs 16.3 months) in favor of adding tucatinib vs placebo to first-line maintenance therapy with trastuzumab and pertuzumab (HR: 0.641; 95% CI: 0.514-0.799; P <.0001).25
It is important to note that only 44% to 46% of patients in the HR-positive subset also received ET while in the study, which was allowed per physician discretion, and could have potentially reduced the absolute PFS in both treatment arms.29
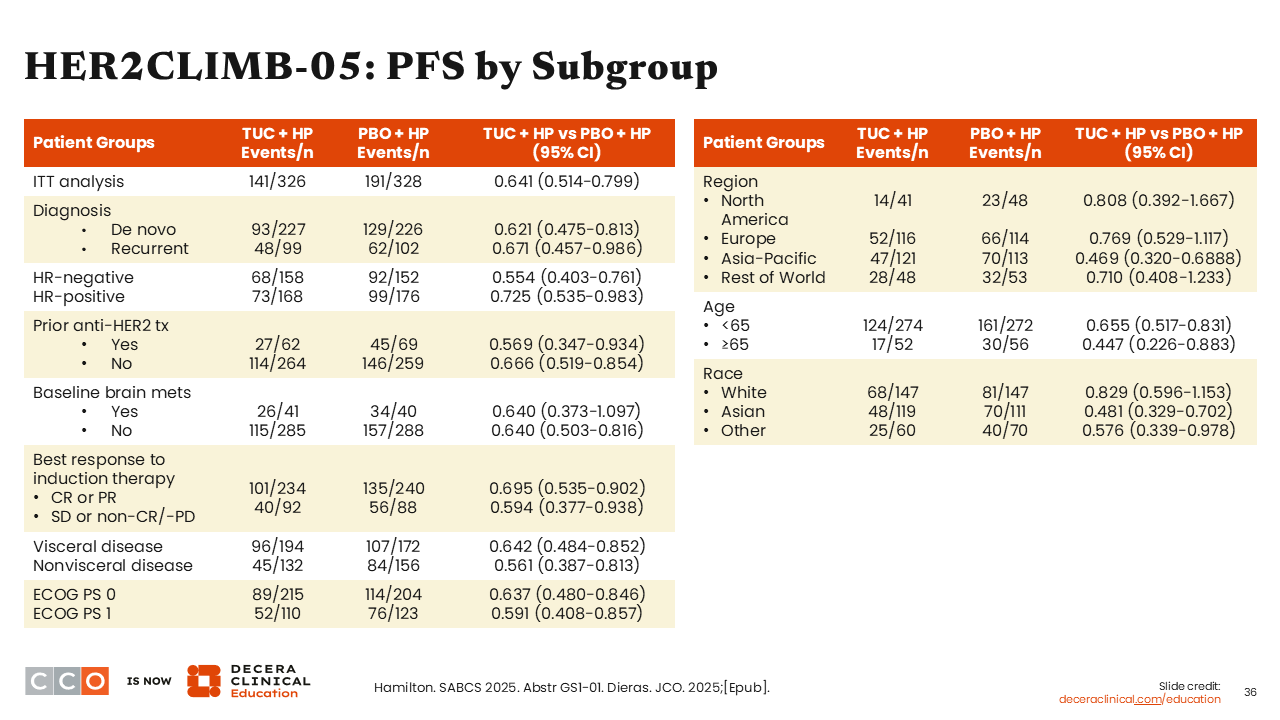
HER2CLIMB-05: PFS by Subgroup
Sara M. Tolaney, MD, MPH:
Across patient subgroups, there was consistent PFS benefit particularly for those with (HR: 0.640; 95% CI: 0.373-1.097) or without (HR: 0.640; 95% CI: 0.503-0.816) brain metastases at baseline, with (HR: 0.642; 95% CI: 0.484-0.852) or without (HR: 0.561; 95% CI: 0.387-0.813) visceral disease, and patients 65 years of age or older (HR: 0.447; 95% CI: 0.226-0.883).25
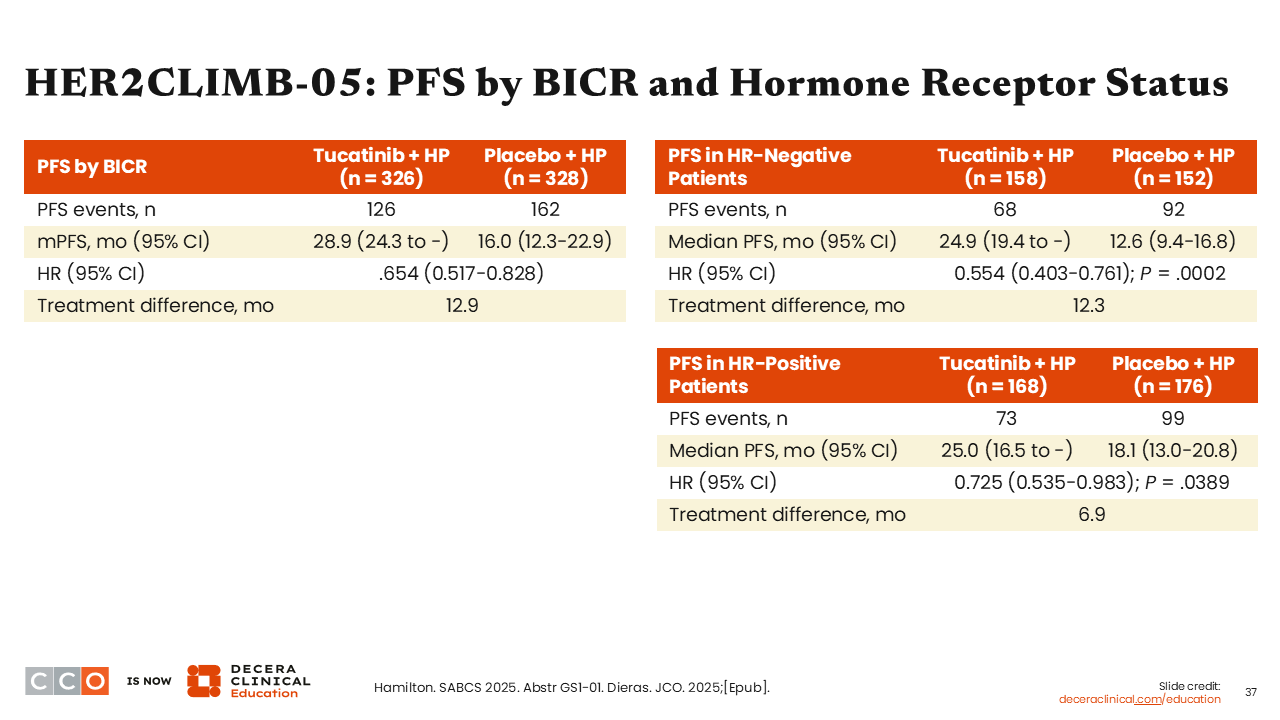
HER2CLIMB-05: PFS by BICR and Hormone Receptor Status
Sara M. Tolaney, MD, MPH:
Another key finding was that the PFS benefit for patients with HR-negative disease showed a larger improvement (HR: 0.554; 95% CI: 0.403-0.761; P = .0002) compared with HR-positive disease (HR: 0.725; 95% CI: 0.535-0.983; P = .0389). What I find interesting is that the median PFS for the tucatinib arm is almost identical for HR-positive and HR-negative disease. It is the control arm that is performing unexpectedly.25
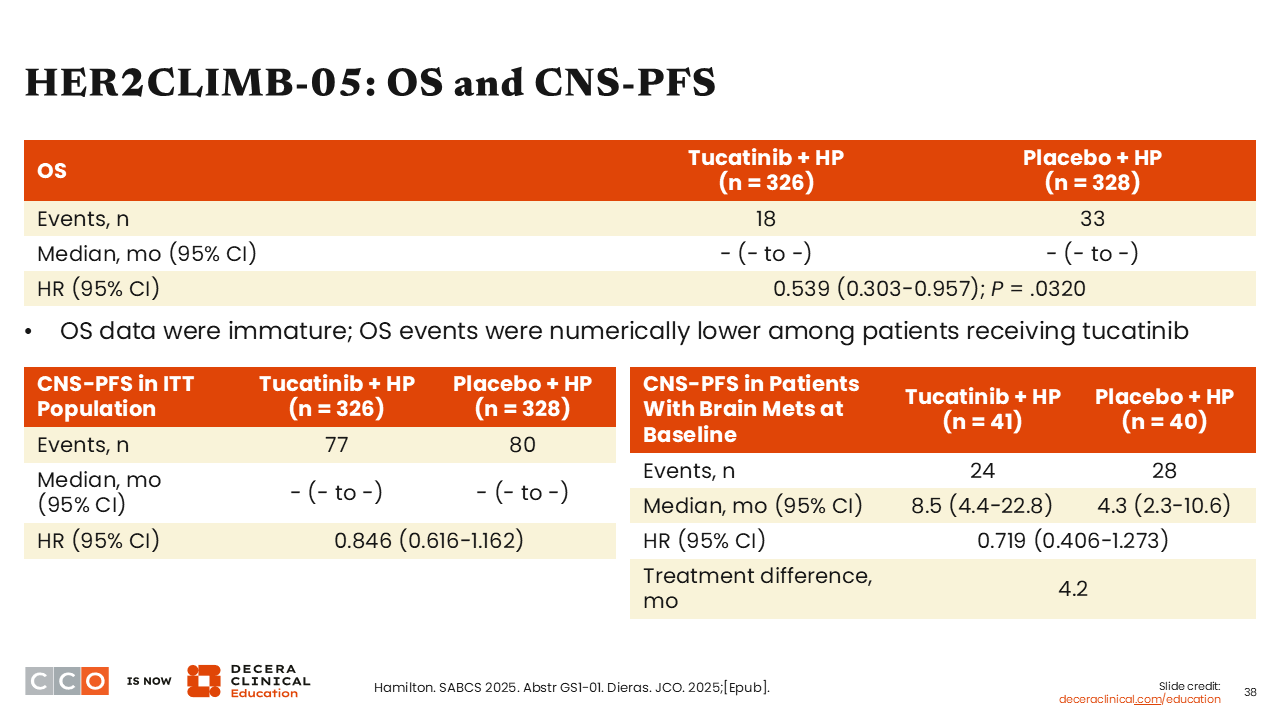
HER2CLIMB-05: OS and CNS-PFS
Sara M. Tolaney, MD, MPH:
Additional analyses for CNS-PFS outcomes were also of interest because of the established survival benefit previously reported in patients with previously treated HER2-positive ABC with brain metastases.30 HER2CLIMB-05, however, is exploring tucatinib in the first-line maintenance setting. That being said, we know that CNS events are often lower in the upfront setting. Study investigators will need longer follow-up to establish a definitive PFS benefit because the number of CNS events separating the 2 arms is quite small at the time of this report. Although there is trend in favor of tucatinib with fewer CNS events at time of progression, the differences are numerically small for the ITT population and patient subgroup with brain metastases.
OS data are highly immature, but there is trend favoring the tucatinib arm (HR: 0.539; 95% CI: 0.303-0.957; P = .0320).25
What I took away from this trial is that adding tucatinib to trastuzumab and pertuzumab as first-line maintenance therapy should be practice changing. Adding tucatinib to first-line maintenance clearly improves PFS across patient subgroups. The question that arises is how do we integrate this combination into the first-line maintenance setting for HER2-positive MBC, where we already have many choices?
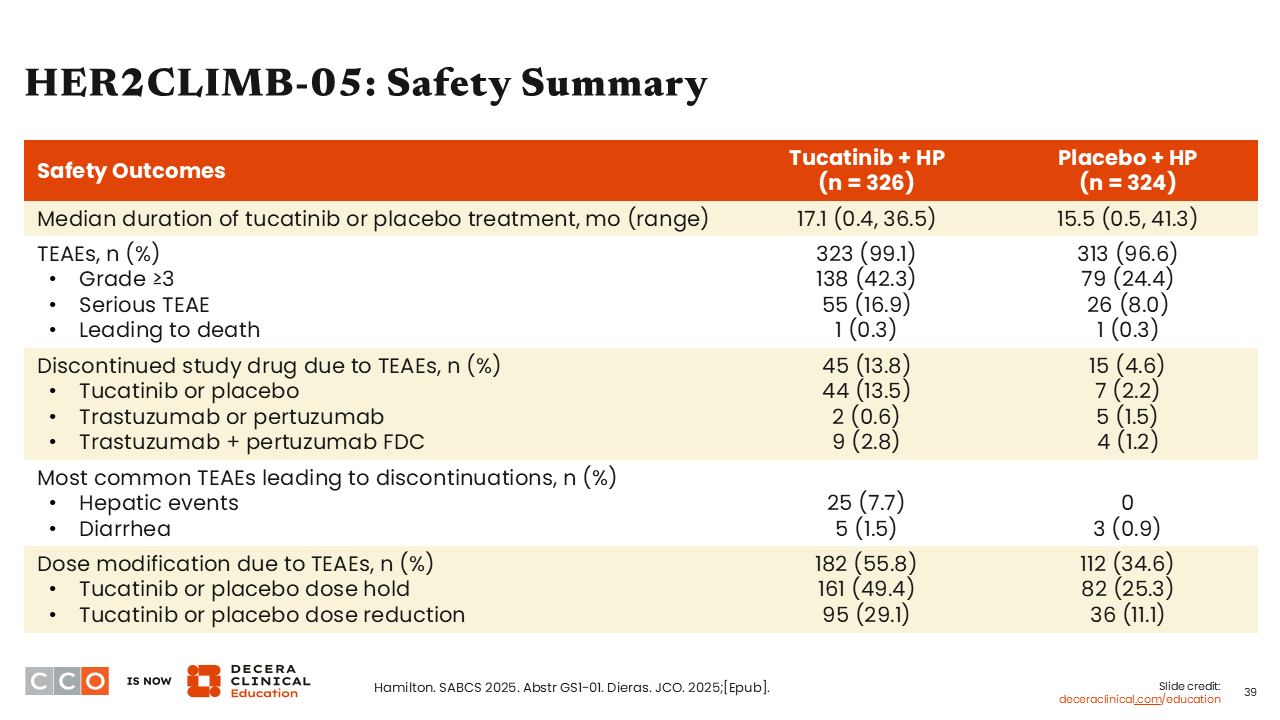
HER2CLIMB-05: Safety Summary
Sara M. Tolaney, MD, MPH:
Turning to the safety data presented for the HER2CLIMB-05 study, we see that diarrhea and hepatic events led to more TEAE discontinuation for the tucatinib arm vs the placebo arm (hepatic events: 7.7% vs 0%; diarrhea: 1.5% vs 0.9%). Moreover, the number of dose modifications were higher with tucatinib (55.8% vs 34.6%), particularly dose holds (49.4% vs 25.3%) and dose reductions (29.1% vs 11.1%).
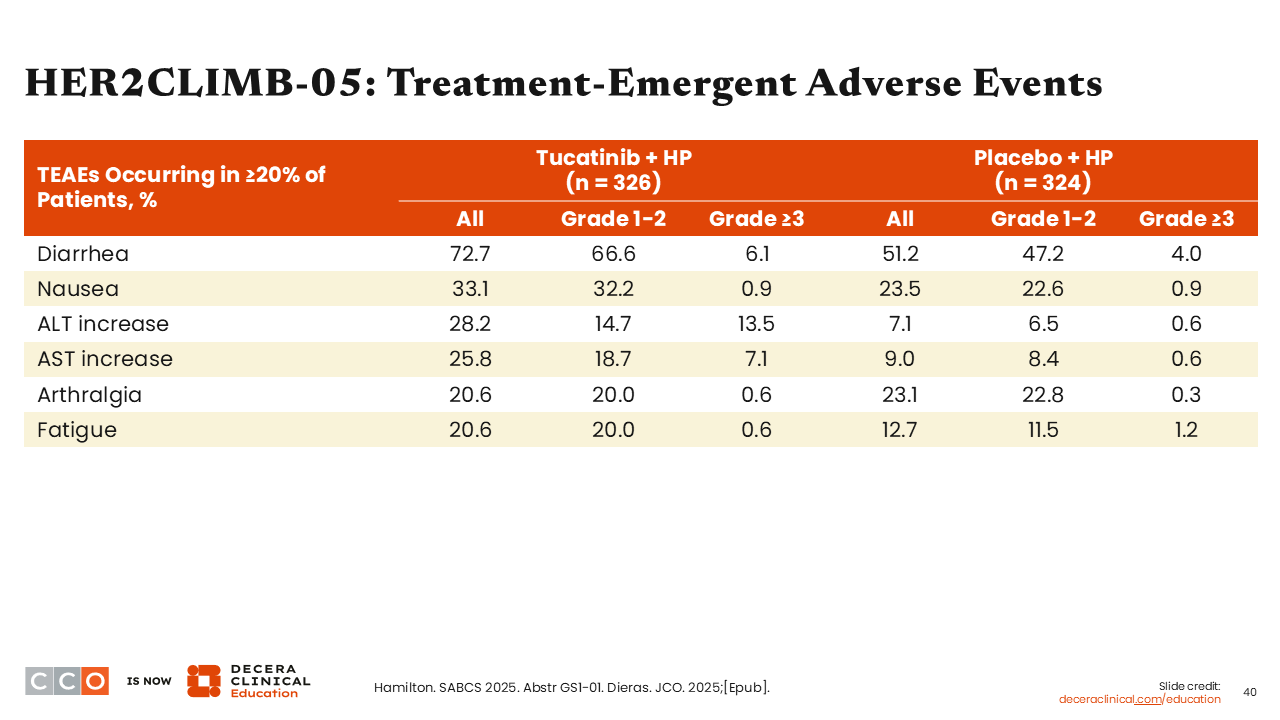
HER2CLIMB-05: Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events
Sara M. Tolaney, MD, MPH:
Overall incidence of any-grade diarrhea was approximately 73% in the tucatinib arm (grade ≥3: 6%) and 51% in the placebo arm (grade ≥3: 4%).
Elevated liver enzymes such as ALT (any grade: 28.2% vs 6.5%; grade ≥3: 13.5% vs 0.6%) and AST (any grade: 25.8% vs 9.0%; grade ≥3: 7.1% vs 0.6%) were comparatively higher in the tucatinib arm vs the placebo arm.
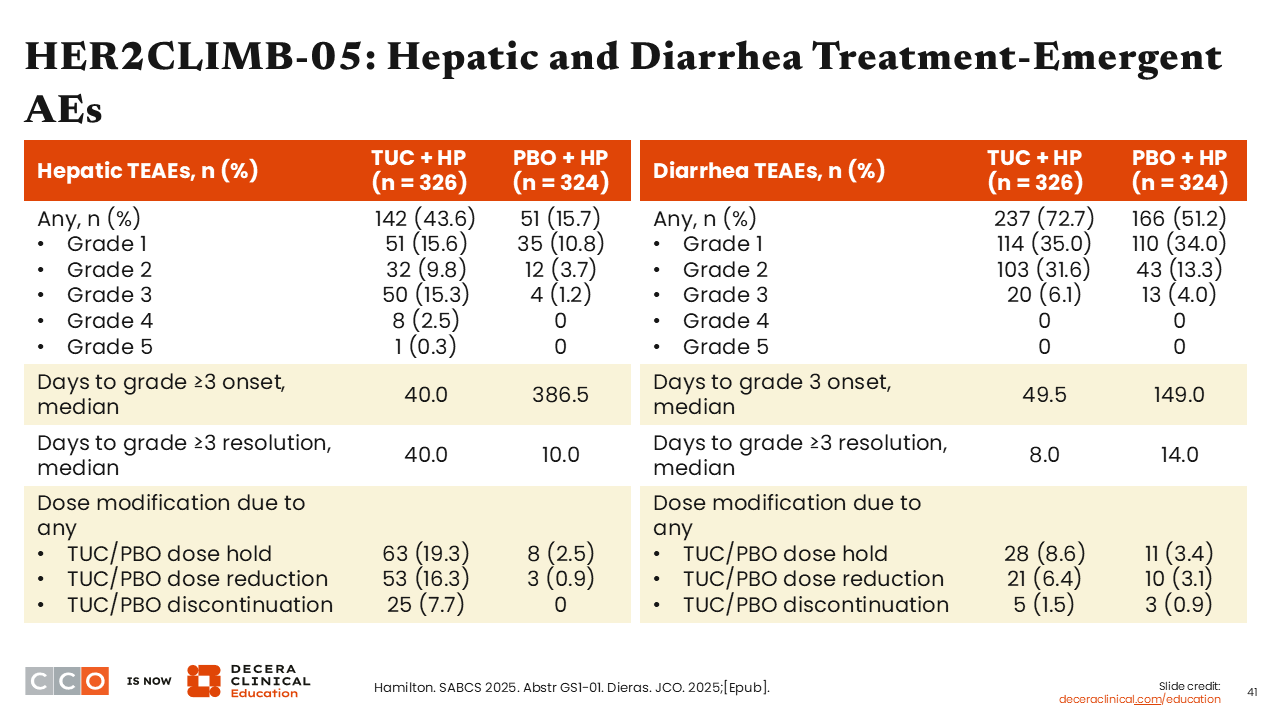
HER2CLIMB-05: Hepatic and Diarrhea Treatment-Emergent AEs
Sara M. Tolaney, MD, MPH:
Study investigators also presented in-depth analyses for the management and resolution of hepatic and diarrhea AEs, which continue to show there is an increased likelihood of experiencing a higher grade or treatment discontinuations due to these AEs with tucatinib-based treatment compared with the control arm. The median onset for grade ≥3 AEs of hepatic toxicity was approximately 40 days and for diarrhea it was 50 days. Of importance, the median number of days for resolution of grade ≥3 AEs of hepatic toxicity was 40 days with tucatinib and 10 days with placebo. The median number of days for grade ≥3 AEs of diarrhea was 8 with tucatinib and 14 with placebo.
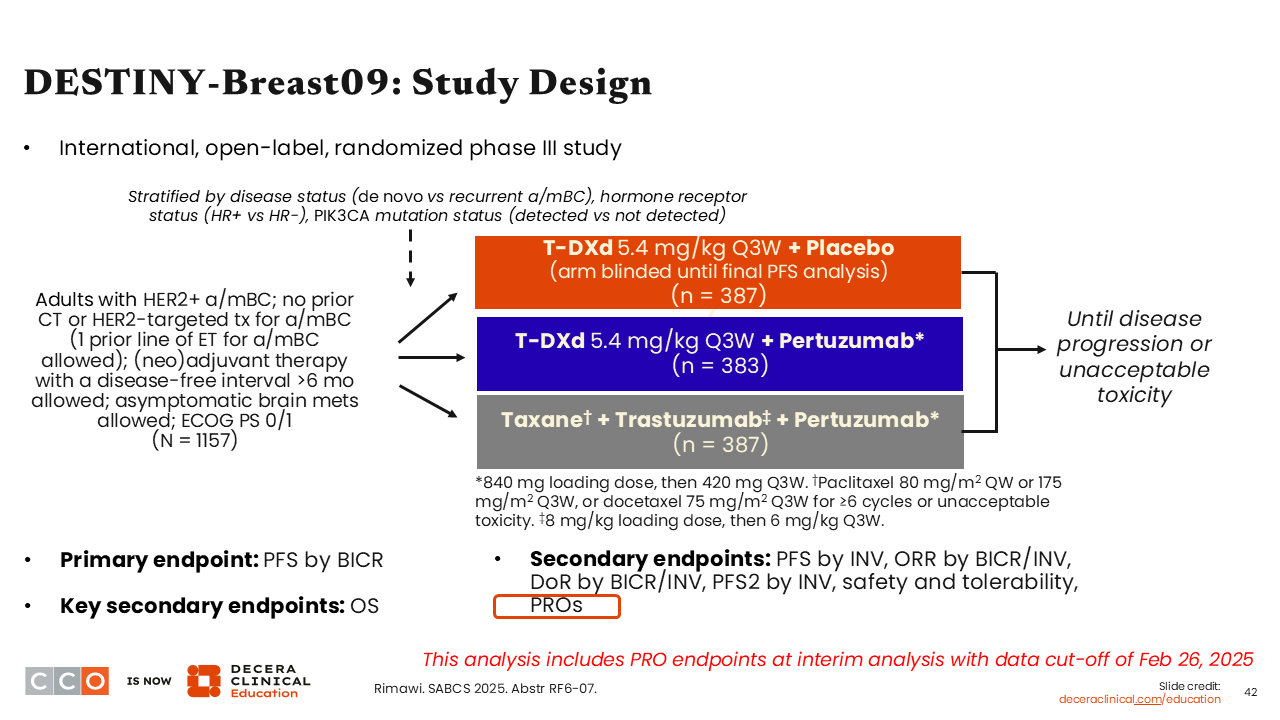
DESTINY-Breast09: Study Design
Sara M. Tolaney, MD, MPH:
Another potential choice for the treatment of HER2-positive MBC in the first-line setting is T-DXd—a HER2-directed ADC therapy currently indicated in combination with pertuzumab as first-line treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic HER2-positive (IHC 3+ or ISH+) breast cancer.31 Approval of this combination is supported by data from the phase III DESTINY-Breast09 trial which evaluated T-DXd in combination with placebo or pertuzumab vs THP in patients with HER2-positive ABC or MBC in the first-line setting, although 1 prior line of ET was allowed. In an interim analysis, investigators reported a significant improvement in PFS with T-DXd plus pertuzumab vs THP (median PFS: 40.7 vs 26.9 months; HR: 0.56; P <.00001).
An ongoing question when considering T-DXd earlier in the disease course is regarding the impact on patients’ quality of life. One might imagine that receiving upfront induction treatment with THP followed by maintenance with trastuzumab and pertuzumab might be better tolerated because patients are not continuing to get cytotoxic therapy until time of disease progression. Therefore, investigators from the DESTINY-Breast09 trial set out to explore the impact of T-DXd plus pertuzumab in the form of patient PROs and these data were presented at SABCS 2025.32
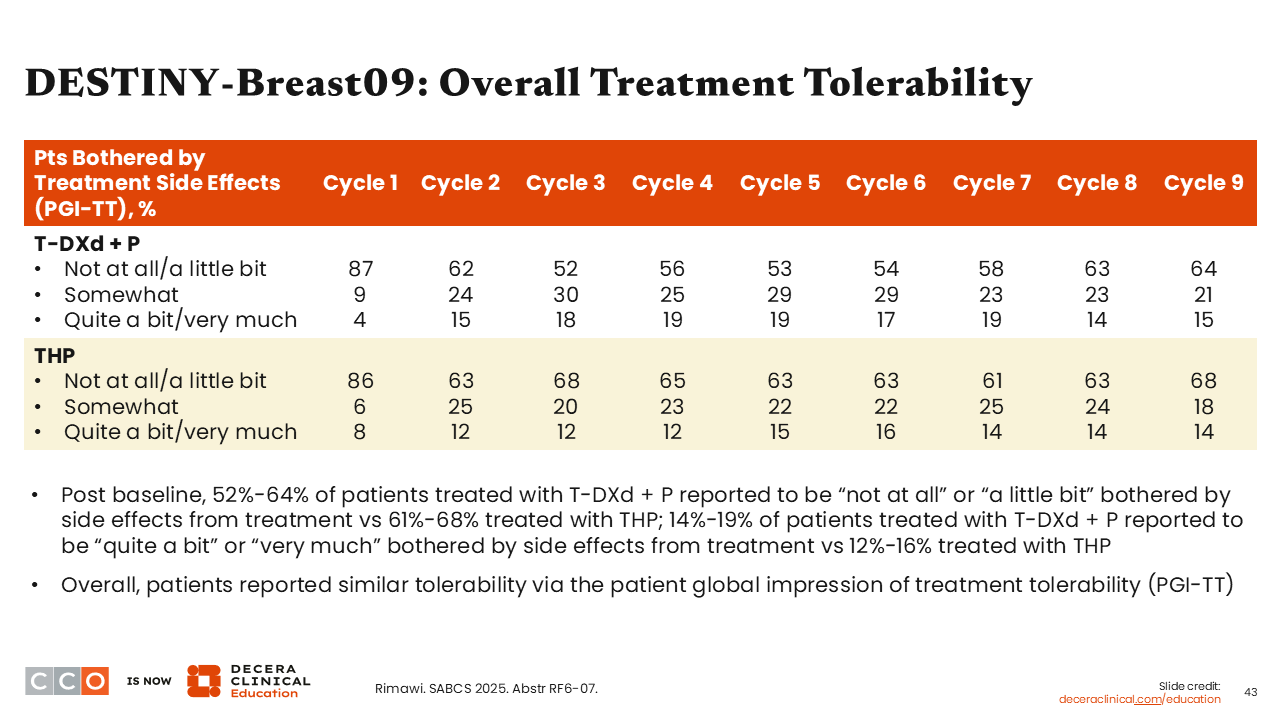
DESTINY-Breast09: Overall Treatment Tolerability
Sara M. Tolaney, MD, MPH:
What I found most interesting about these data was that there was a similar proportion of patients who reported being “not at all” or “a little bit” bothered by the AEs from their treatment in the T-DXd plus pertuzumab arm compared with the triple-therapy arm from cycle 1 to cycle 2, but the numbers were modestly lower for T-DXd plus pertuzumab vs THP from cycle 3 through cycle 6, then similar again thereafter.
There also were similar reports of tolerability overall via the patient global impression of treatment tolerability scale. That result was surprising to me, because I did not expect it to be so.32
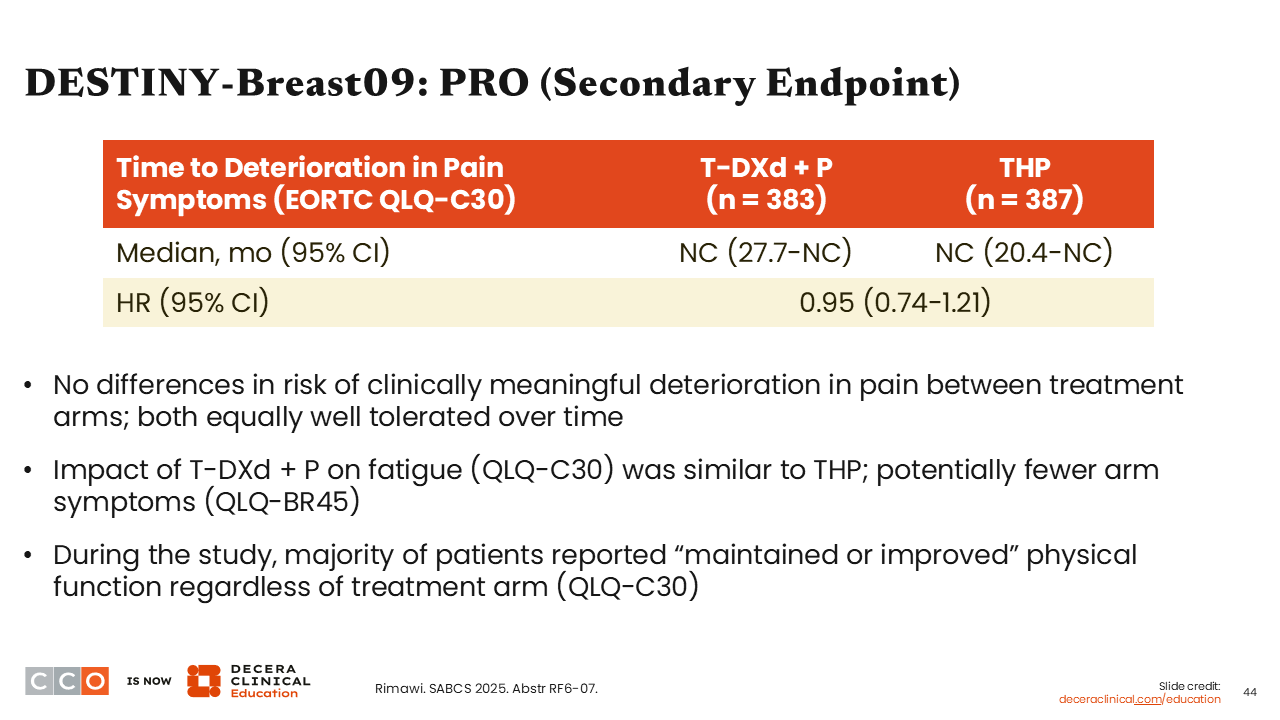
DESTINY-Breast09: PRO (Secondary Endpoint)
Sara M. Tolaney, MD, MPH:
When we look specifically at the secondary endpoint of PROs, there were no differences in risk of clinically meaningful deterioration in pain between both study arms (HR: 0.95; 95% CI: 0.74-1.21). Again, data showed treatment arms were similarly tolerated over time.
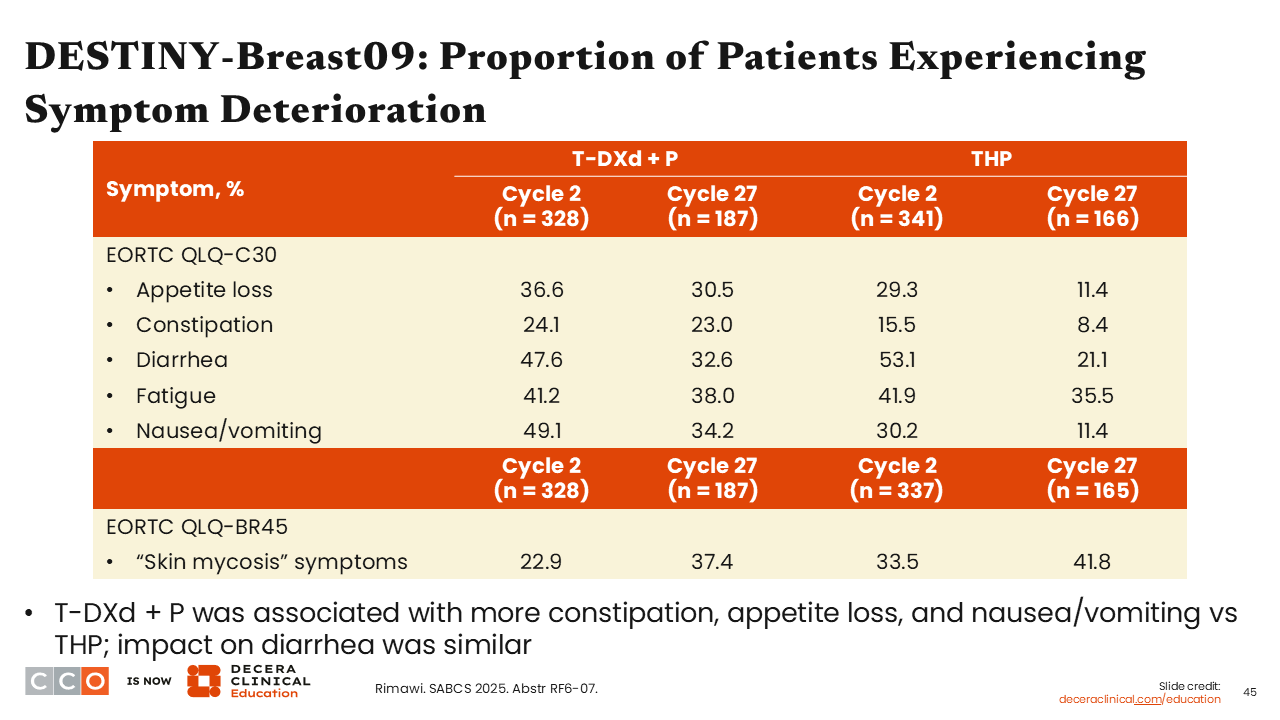
DESTINY-Breast09: Proportion of Patients Experiencing Symptom Deterioration
Sara M. Tolaney, MD, MPH:
Patients reported a greater impact of gastrointestinal-related AEs with T-DXd plus pertuzumab vs THP starting at cycle 2. These AEs included appetite loss (36.6% vs 29.3%), constipation (24.1% vs 15.5%), and nausea/vomiting (49.1% vs 30.2).